Android Low Energy Bluetooth Gatt Connection Tutorial: Implementing with Kotlin
Introduction
I spent some time reviewing the Low Energy Bluetooth connection I implemented in previous work.
Because I was worried I might forget,
I wanted to revisit and document it,
hoping it can also help those who need to implement it.
After Android 12, new permission-related handling was added, so take note!
Here is how I handled it, for your reference:
The ultimate goal is this
To integrate with previous Jetpack Compose practices
Making the data real and existent
And finally, to connect to Gatt Bluetooth

Basic Concepts
First, let's introduce
the methods of Bluetooth scanning
There are roughly three
BluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery() -> Scans both classic Bluetooth and BLE Bluetooth
BluetoothAdapter.startLeScan() -> Used to scan Low Energy Bluetooth ---- Deprecated
BluetoothLeScanner.startScan() -> New BLE scanning method
However, looking at the API notes
startLeScan is currently deprecated
It was deprecated in API 21
I also checked various APIs for discovering Bluetooth devices for comparison
- The scanning process usually runs for 12 seconds
- It is an asynchronous call
-
Executed through registering broadcasts for different steps, such as:
ACTION_DISCOVERY_STARTED -> When Discovery starts ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED -> When Discovery finishes BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND -> When a Bluetooth device is found </a> </li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">When connecting to a Bluetooth device It cannot be in startDiscovery You need to call cancelDiscovery() to end the discovery </a> </li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)"> Discovery is not managed by the Activity But by the system service So, to be safe, you must use cancelDiscovery() To ensure Discovery is not running To avoid the device still being in Discovery when connecting to a Bluetooth device </a> </li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">Discovery can only find currently discoverable Bluetooth devices </a> </li><li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">Observe if ACTION_STATE_CHANGED is STATE_ON If the current Bluetooth state is not STATE_ON, the API will return false Used to determine if the current state is one where updated values can be obtained <img src="/images/bluetooth/android_state.png" alt="Cover" class="w-full prose-img" loading="lazy" decoding="async"> </a> </li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">If the target version used is less than or equal to Build.VERSION_CODES#R You need to request the Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH_ADMIN permission from the user <img src="/images/bluetooth/android_R.png" alt="Cover" class="w-full prose-img" loading="lazy" decoding="async"> </a> </li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)"> If the target version used is greater than or equal to Build.VERSION_CODES#S You need to request the Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH_SCAN permission from the user <img src="/images/bluetooth/android_S.png" alt="Cover" class="w-full prose-img" loading="lazy" decoding="async"> </a> </li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">Additionally You can request the Manifest.permission#ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission To increase the types of interactive Bluetooth devices Of course, you can also add the usesPermissionFlags="neverForLocation" tag in <b>uses-permission</b> To avoid requesting location permissions But the types of devices that can be searched will be limited </a> </li> </ol> </div> <div class="c-border-content-title-4">fun startScan ( callback:ScanCallback )</div> <div class="table_container"> <ol class="rectangle-list"> <li><a href="javascript:void(0)">Start Bluetooth LE scan, scan results will be returned via callback</a></li> <li><a href="javascript:void(0)">Because this does not include filters, The default power-saving mode will stopScan when the screen is off, And resume when the screen is turned back on</a></li> <li><a href="javascript:void(0)">If the target version used is greater than or equal to Build.VERSION_CODES#Q, You need to request the Manifest.permission#ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission from the user</a></li> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">If the target version used is less than or equal to Build.VERSION_CODES#R, You need to request the Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH_ADMIN permission from the user <img src="/images/bluetooth/android_R.png" alt="Cover" class="w-full prose-img" loading="lazy" decoding="async"> </a> </li> <li><a href="javascript:void(0)">If the target version used is greater than or equal to Build.VERSION_CODES#S, You need to request the Manifest.permission#BLUETOOTH_SCAN permission from the user <img src="/images/bluetooth/android_S.png" alt="Cover" class="w-full prose-img" loading="lazy" decoding="async"> </a></li> <li><a href="javascript:void(0)">Additionally, you can request the Manifest.permission#ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission, to increase the types of interactive Bluetooth devices, of course, you can also add the usesPermissionFlags="neverForLocation" tag in <uses-permission>, to avoid requesting location permissions, but the types of devices that can be discovered will be limited</a></li> </ol> </div> <div class="c-border-content-title-4">fun startScan(filters:List<ScanFilter>,settings:ScanSettings,callback:ScanCallback)</div> <div class="table_container"> <ol class="rectangle-list"> <li> <a href="javascript:void(0)">Features include the six items from the above startScan ( callback:ScanCallback ) </a> </li> <li> <a href="https://developer.android.com/reference/android/bluetooth/le/ScanFilter" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"> Use ScanFilter to filter the scan results, mainly supporting the following items, <img src="/images/bluetooth/android_filter.png" alt="bluetooth android filter" style="width: 80%" loading="lazy" decoding="async" class="prose-img"> </a> </li> <li><a href="https://developer.android.com/reference/android/bluetooth/le/ScanSettings#summary" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"> Also use ScanSettings to set how to handle the returned callback, such as: return each successfully filtered data, only return the first successfully filtered data... etc.</a></li> </ol> </div> ## Actual Development: How to Perform Bluetooth Scanning Add the required permissions mentioned above in the manifest <script src="https://gist.github.com/waitzShigoto/fc855c0ab9c4667df49b253595744d08.js"></script> <div class="c-border-content-title-4">Request Permissions in the Code</div> Below is an extension that can be used universally ```kotlin requestMultiplePermissions(Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,...Obtain an Instance of BluetoothAdapterprivate val bluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter? = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter()Register to Receive BroadcastsRegister to listen for BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND
val filter = IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND) requireContext().registerReceiver(receiver, filter)Extend a BroadcastReceiver
and use the receiver type to return the result bleDevice
private val receiver = DeviceListBoardCast { bleDevice -> deviceViewModel.addDevice(bleDevice) }其中取資料的方式是,到時候掃描出來的資料可以從這幾個拿
val device: BluetoothDevice = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE)!! val rssi = intent.getShortExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_RSSI, Short.MIN_VALUE).toInt() val uuidExtra = intent.getParcelableArrayExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_UUID)繼承的BroadcastReceiver實作
開始進行掃描前面已經拿到bluetoothAdapter跟註冊廣播監聽了
所以開始分別可以用startDiscovery、cancelDiscovery 來開始或結束掃描
bluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery() bluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery()這個函式
主要是進行掃描的開關
並搭配viewmodel與coroutine
做到用viewmodel紀錄刷新狀態,並透過coroutine掃描指定秒數 x 秒
如果不需要用到那麼複雜的話
直接用startDiscovery、cancelDiscovery去開發就行了
掃描的結果會返回剛剛DeviceListBoardCast {}內,
這邊根據自己專案去調整就行
我是用viewmodel來觀察資料
private val receiver = DeviceListBoardCast { bleDevice -> deviceViewModel.addDevice(bleDevice) }實際開發:如何進行藍芽連線
主要概念是建好app本地的service,當跟藍芽綁定時,就能互相溝通這邊使用service的方式去串接
首先建立一個service
並建立Binder
用來onBind時返回實例給fragment去調用
初始化必需的class類別在該service內創建一個 initialize()函式
用在之後bindservice時可以調用初始化
寫好callback,到時候藍芽狀態返回就能收到接著寫個gattCallback實例
這邊主要是onConnectionStateChange、onServicesDiscovered、onCharacteristicRead
分別是當有新的連接狀態改變、新的服務被發現、新的東西讀到後
返回的callback
這邊主要可以根據你的需求
去做判斷
這段記錄下連線中可能的情況:-
onConnectionStateChange ->返回藍芽狀態
-
當執行discoverServices() 去找現有的ble
當找到會進onServicesDiscovered
- 有個方法setCharacteristicNotification
這個是去啟用notify
去找特定的Characteristic
(這邊Characteristic就看跟硬體的協議或定義)
When the Bluetooth device value changes, it will notify you with onCharacteristicChanged
- Then, writeCharacteristic allows you to write values into the specified Characteristic
Similarly, when there is a result, it will go to
onCharacteristicWrite
gattCallback example:
Start ConnectionCreate a connect functionThe main part is to connect using the following two lines
val device = bluetoothAdapter!!.getRemoteDevice(address)and
bluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(this, false, gattCallback)Pass the address you want to connect to
Get the BluetoothDevice you want to connect to
Then use the connectGatt method in the device to bind the Gatt device
Of course, you also need to pass in the gattCallback written earlier
The previous part is just a series of null checks
To ensure the app does not crash due to null
In the instantiation of gattCallback,
you will find a method named broadcastUpdate.
This method is mainly used to send broadcast messages,
you can define what to do in different situations according to your needs,
or what broadcast messages to return.
Simple connection and device search
That's about it
Next, the most important thing in Bluetooth is communication between terminals
So if you want to send and receive data
You need to find the service and characteristic
Here is a diagram
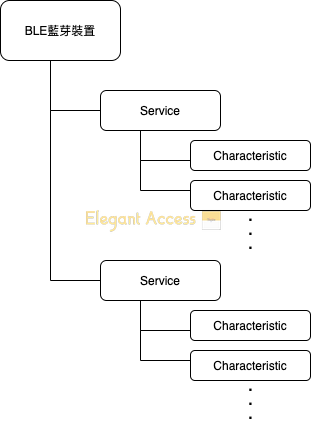 This is a general relationship diagram when connecting Bluetooth
This is a general relationship diagram when connecting Bluetooth
So we find it through the following method:
Bring in the gatt service obtained through the broadcast earlier
Then you can traverse to get the characteristic
Since the official Android has already wrapped the characteristic class for you
To read, you just need to call the relevant function:
And it will return to you in the previously defined BluetoothGattCallback
onCharacteristicRead
You just need to define the broadcast reception to get the data
Additionally, there is also a notify method in Bluetooth:
Similarly, it returns the result
In BluetoothGattCallback
Check onCharacteristicChanged
If you want to see how to capture Bluetooth packets through third-party tools
You can refer to:
Bluetooth Module Notes: Includes Classic Bluetooth (BT) and Low Energy Bluetooth (LTE)
Classic Bluetooth (BT)Includes Bluetooth 1.0 / 1.2 / 2.0+EDR / 2.1+EDR / 3.0+EDR and other developments and improvementsGenerally refers to modules below Bluetooth 4.0
Typically used for data transmission with larger volumes
Examples: voice, music, higher data volume transmission, etc.
Classic Bluetooth modules can be further subdivided into
Traditional Bluetooth modules and High-Speed Bluetooth modules
Traditional Bluetooth modules were introduced in 2004
The main representative is the module supporting the Bluetooth 2.1 protocol
Traditional Bluetooth has 3 power levels
Class1 / Class2 / Class3
Supporting transmission distances of 100m / 10m / 1m respectively
High-Speed Bluetooth modules were introduced in 2009
The speed increased to about 24Mbps
Eight times that of traditional Bluetooth modules
Low Energy Bluetooth Module (BLE)Generally refers to modules of Bluetooth 4.0 or higher
Bluetooth Low Energy technology is low-cost, short-range
Can operate in the 2.4GHz ISM radio frequency band
Because BLE technology uses a very fast connection method
It can usually be in a "non-connected" state (saving energy)
Android phones with Bluetooth 4.x are all dual-mode Bluetooth (both Classic Bluetooth and Low Energy Bluetooth)
Kotlin + Jetpack Compose Bluetooth App Example
Finally, I wrote an example before, and recently organized it. Those who need it can refer to it You can refer to this article
-
 [Android][Kotlin] How to Capture Bluetooth Packet Logs on Android Phones
[Android][Kotlin] How to Capture Bluetooth Packet Logs on Android Phones