【Android】Using Google MLKit & Android X Camera to Implement a Fast QR Code Scanner on Android
If you want to see how the code is written directly, you can: Go to Code Analysis
In this project, Kotlin, Google’s MLKit, and the native AndroidX camera are used to implement the QR scanner.

In the past, we used some third-party libraries to create QR code scanners
such as zxing, zbar, etc.
Recently, in a project, QA feedback indicated that the current QR code scanner’s accuracy was not very high.
So I looked into it and tested it, and finally understood why the accuracy was not very high.
In fact, it was because:
The project used the old android.hardware.Camera with zbar to parse QR codes
and scanned from a side angle or from a distance.
This made the QR code scanner feel slower compared to iOS.
So I decided to try implementing it using Google’s MLKit.
- This API requires
Android API 21or above. - The API provides two versions
One can dynamically download the module from gms
One uses the module that comes with the library, as shown: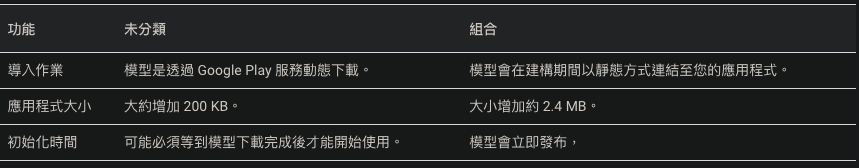
- I referred to examples and used the new native camera library
androidx.camerawithML Kit.
Compared to the original project usingzbarwithandroid.hardware.Camera:
↪ Both camera libraries are supported from Android API 21 and above.
↪ The version usingzbarwithandroid.hardware.Camerahad three workarounds.
I suspect the original project or previous examples used this approach to solve camera initialization issues in the activity.
So they wrote it like this:
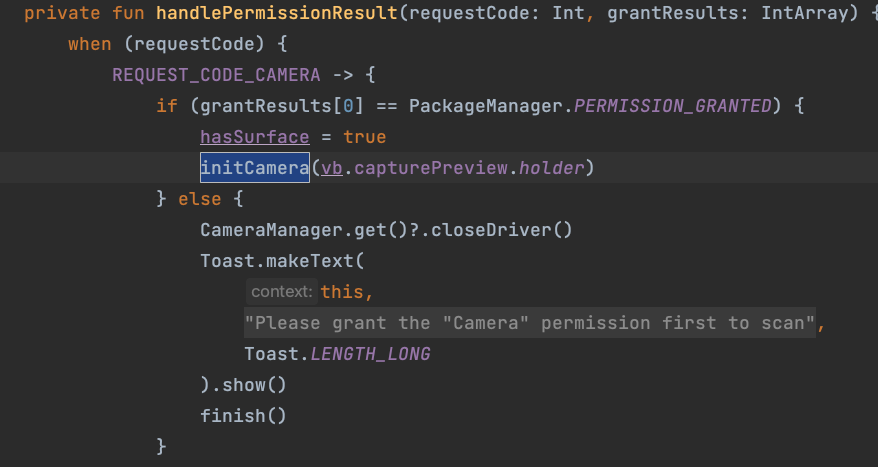
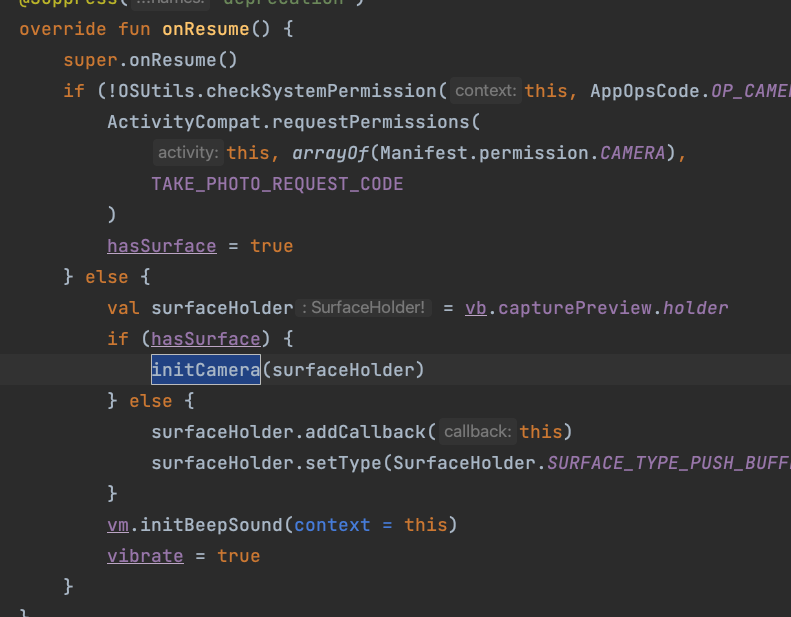
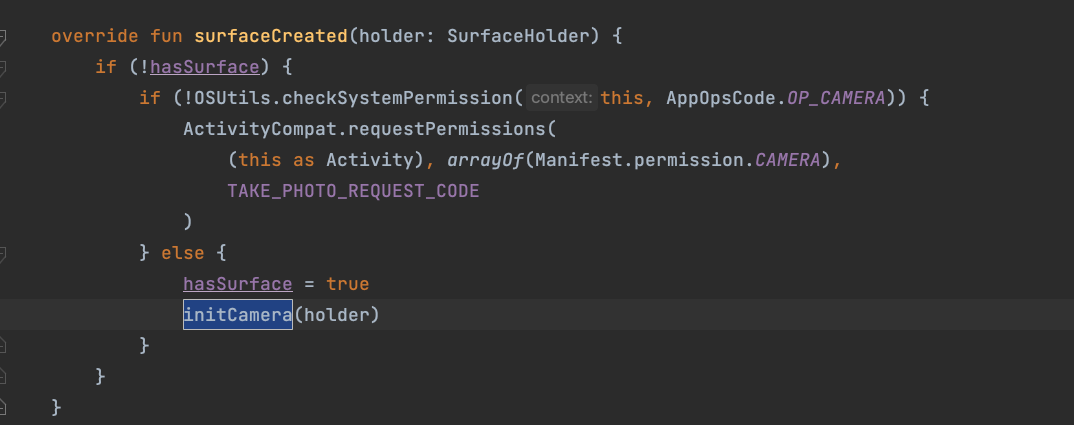
↪ After looking into it,android.hardware.Camerais not thread-safe and has been @Deprecated.
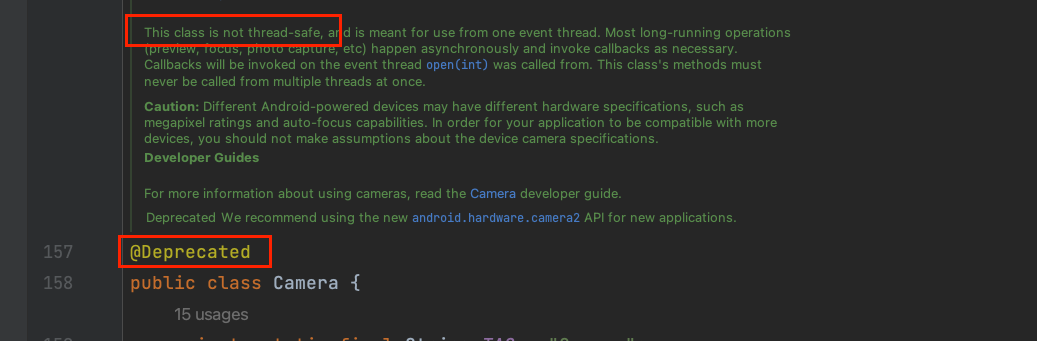
↪ On the other hand, the newandroidx.camera.core.Cameracomes with lifecycle management to handle camera lifecycle issues.
This can avoid some strange lifecycle problems.
✅ So I speculate that switching to the newandroidx.camera.core.Cameracan more effectively avoid lifecycle issues (because you can control it yourself). - The new androidx.camera.core.Camera comes with lifecycle management to handle camera lifecycle issues, avoiding some strange lifecycle problems.
- The scanner decoding uses MLKit’s BarcodeScannerOptions.
It enhances the types of barcodes that can be parsed.
You can refer to this link for the supported formats. Below is the scanner decoding code: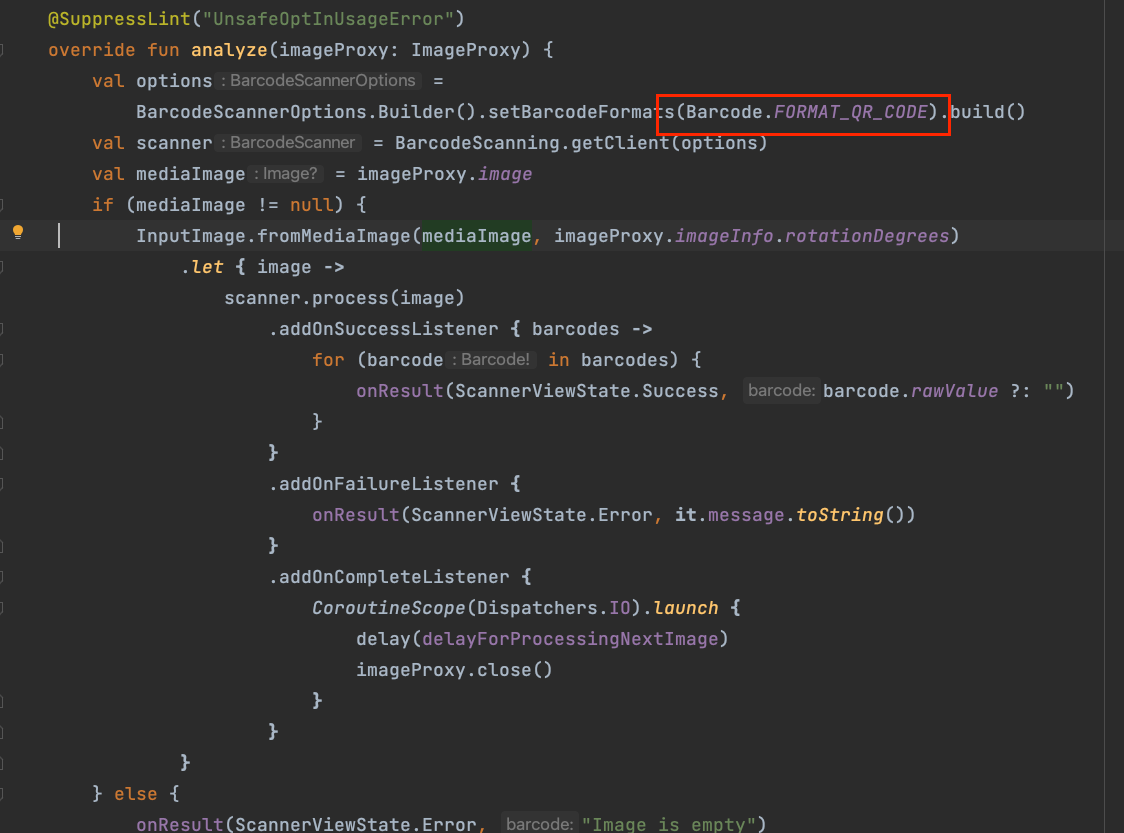
-
Tested on
LG K520 Android 11 - The overall runtime of the camera on
LG K520 Android 11did not differ much
In practice, frominit cameratoparsing QR codetakes about 1 second
However, it can avoid thecamera crash risk caused by lifecycle -
The actual test shows a slightly faster response speed compared to the original solution (not noticeable on better phones, minimal difference)
For example,zbar+android.hardware.Camerawill completelyfocusbefore starting to decode the QR code
mlkit+androidx.camera.core.Cameracan start decoding the QR codehalfway through focusing - The image on the left uses
zbar, and the right usesML kit(this gif is slowed down to0.25x) androidx.camera.core.Cameracan handle lifecycle-related issues
Slowing down the new solution to0.25xmakes it feel like:waiting for a while before displaying the camera(right image)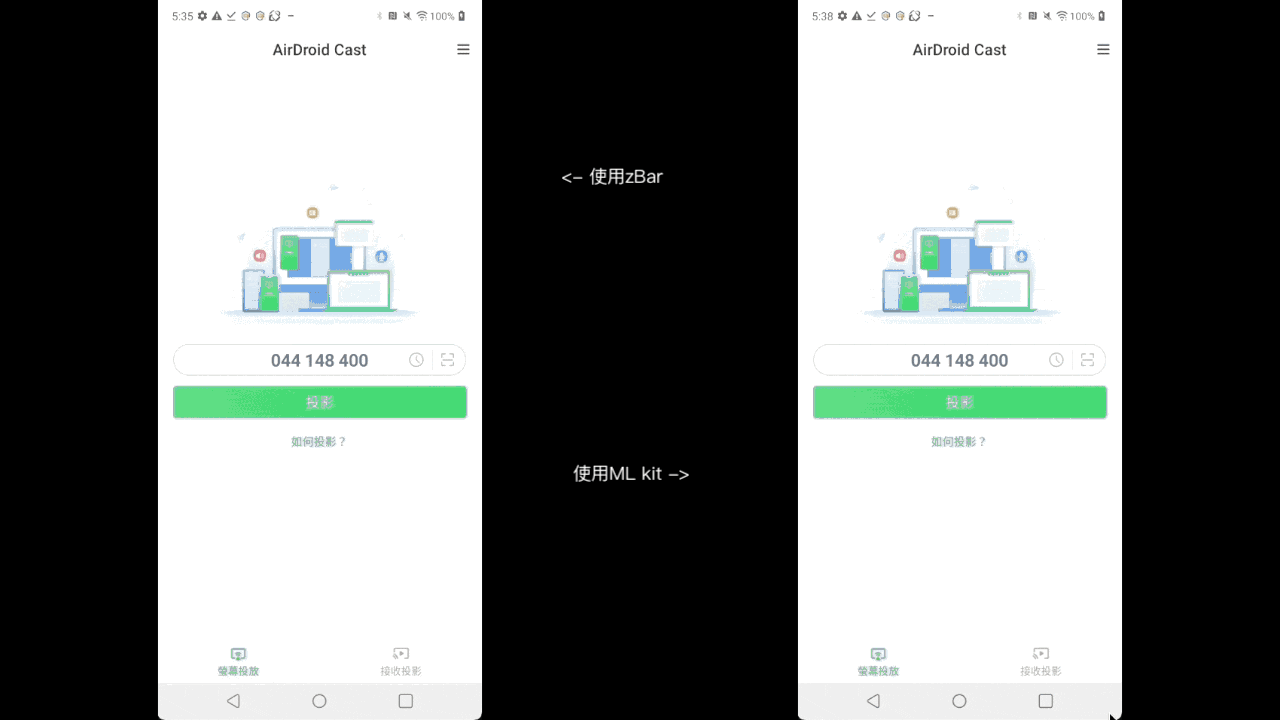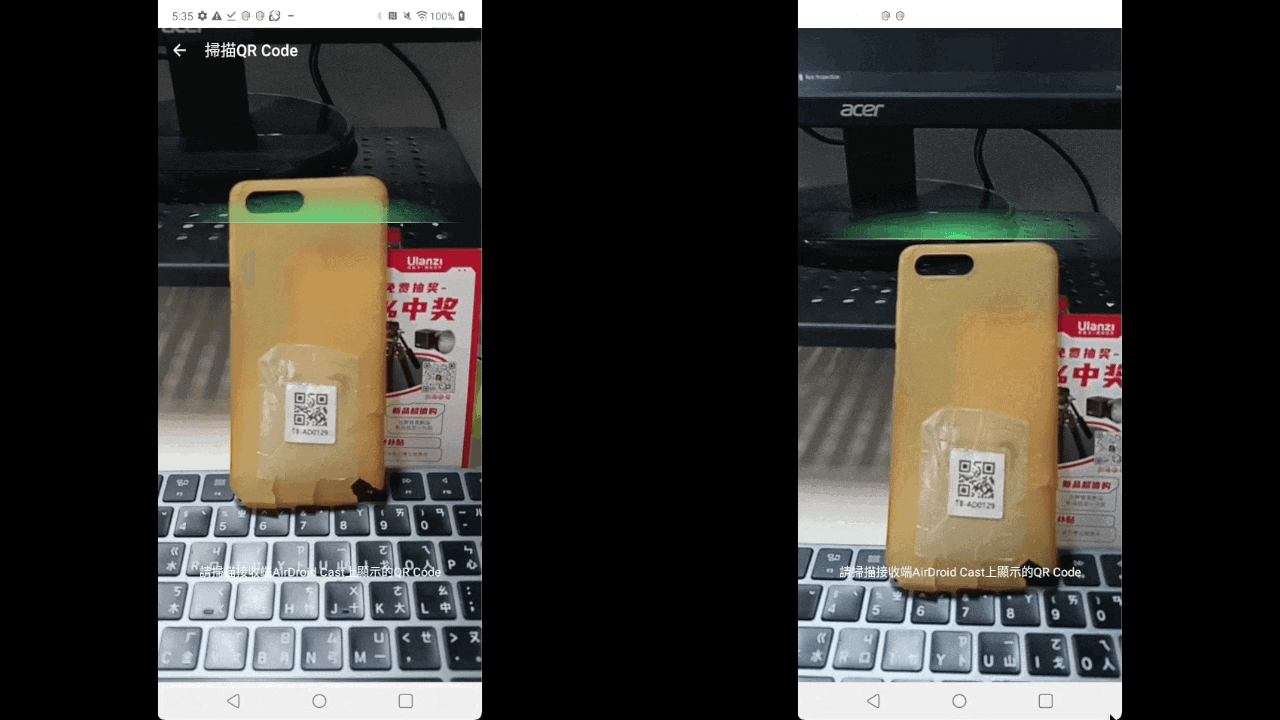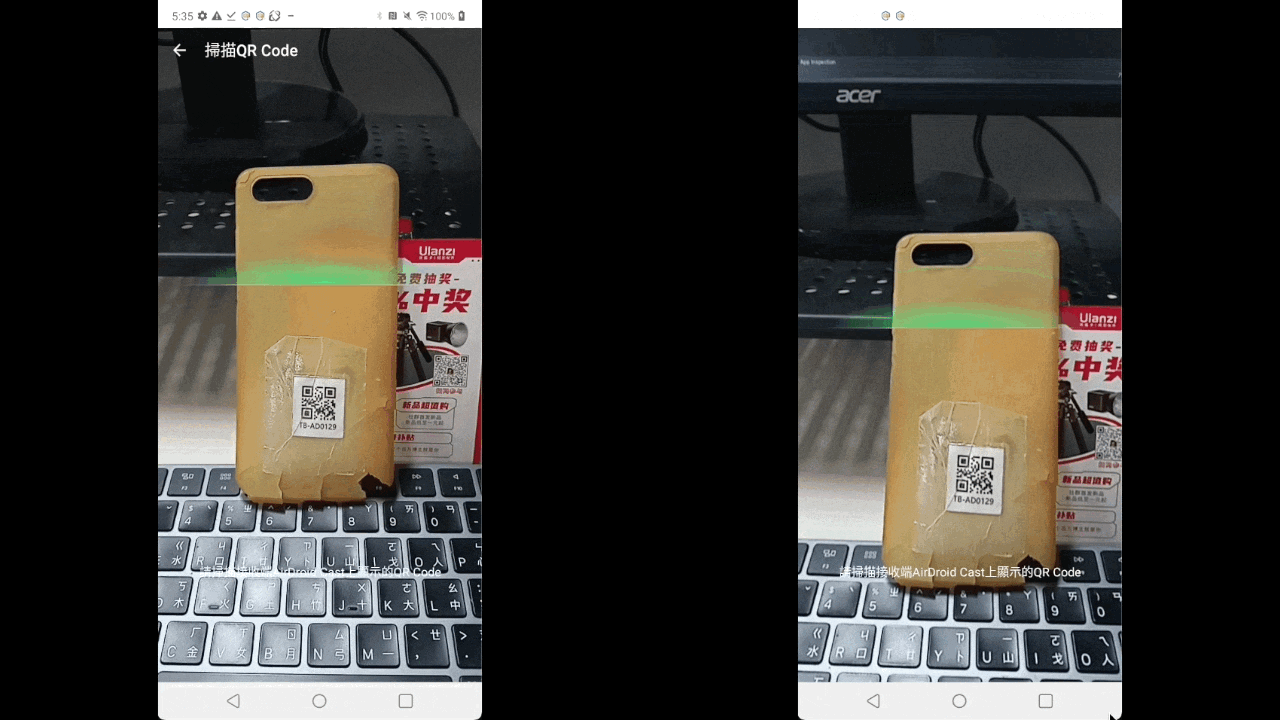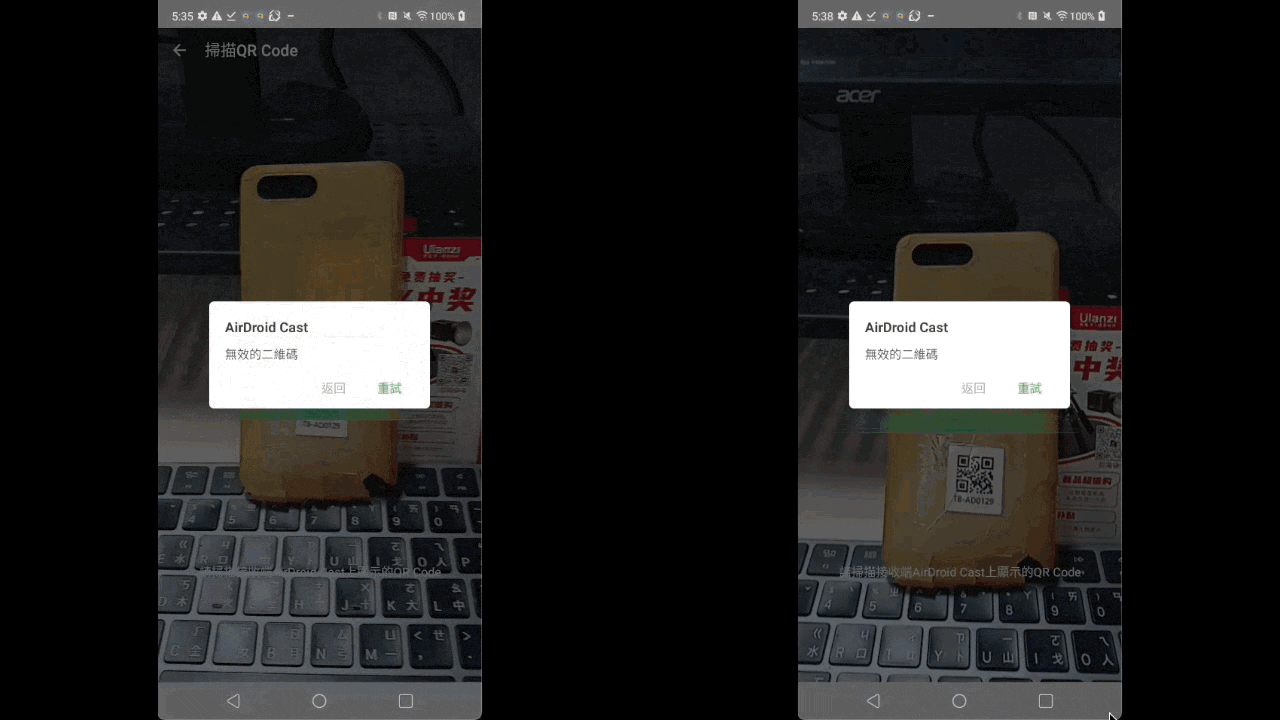
- However, the noticeable improvement is that it is easier to scan when using odd angles or when the camera is farther away
- Add target resolution setting when creating ImageAnalysis
.setTargetResolution(Size(screenResolutionForCamera.x, screenResolutionForCamera.y)) - The screenResolutionForCamera is set using the screen resolution to set the camera target resolution
The difference between setting the camera target resolution or not ishigher success rate of scanning from a distance Additionally: the API Java doc mentions- The default resolution of the camera without TargetResolution set is
640*480 - After setting, there will be a priority to choose the actual
Resolution - Here is the outline: Priority is given to resolutions close to and greater than the Target Resolution > Priority is given to resolutions close to and smaller than the Target Resolution > The ratio of the resolution will be primarily determined by the provided
Size - Therefore, it is speculated that due to
hardware limitations, thedistancethat can be resolved may vary for each device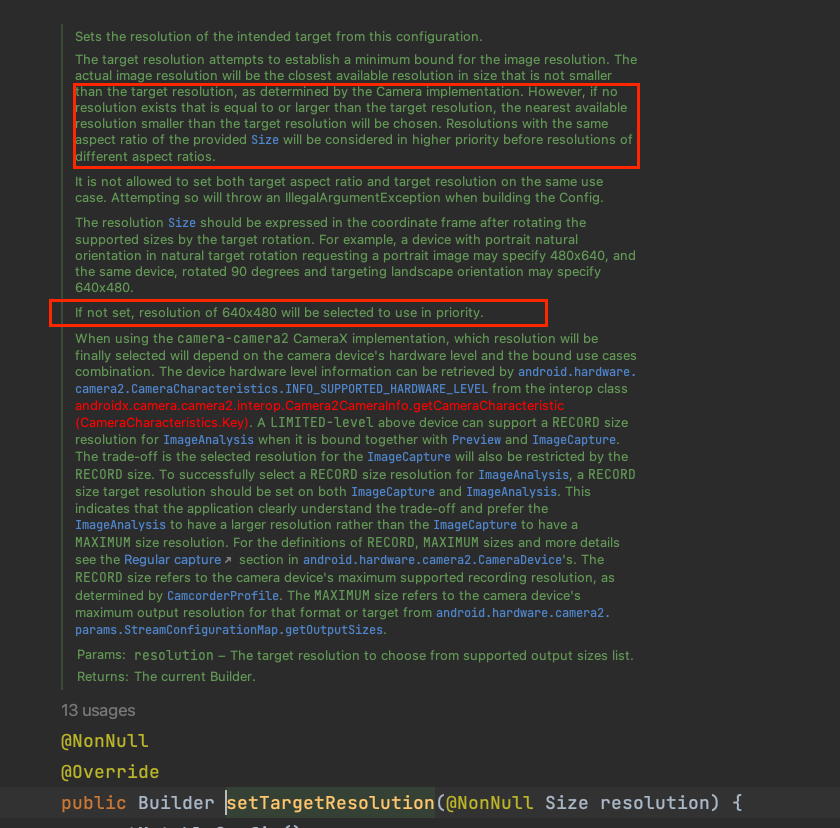
- The default resolution of the camera without TargetResolution set is
- After the above adjustments and optimizations, when asking QA colleagues to help test
They reported that the accuracy of the app has indeed improved compared to the previous version
Upon further inquiry, they said thesuccess rate of scanning from the sideorfrom a farther distanceorbeing detectedhas indeed increased Thus… a problem was solved XD
-
Thank you all for reading the above analysis
I have placed the source code at the top of this article
If interested, you can clone it directly and modify it -
Below I will share the main code analysis of the QR code scanner
Feel free to refer to it if interested
Code Explanation
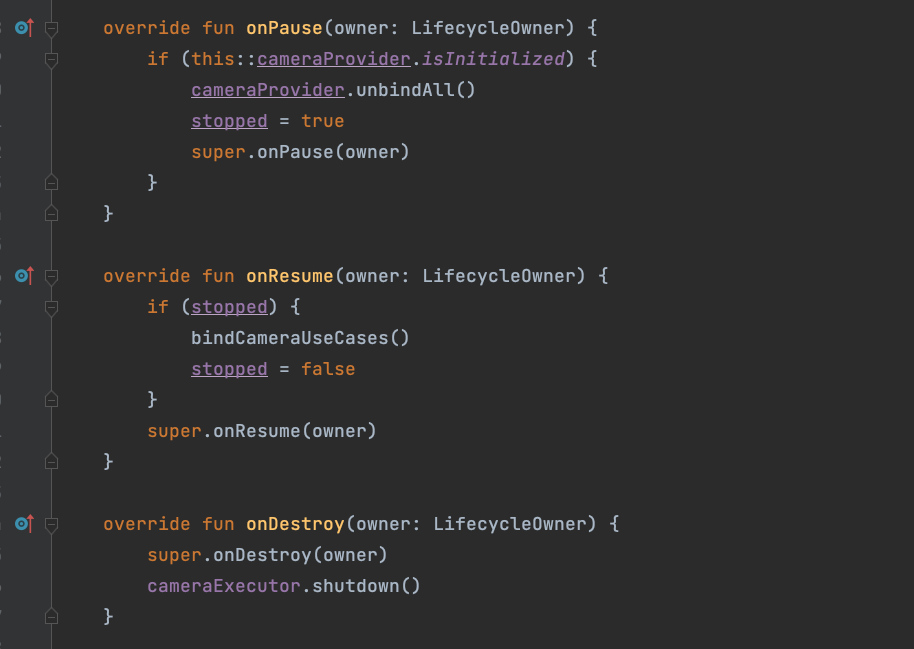
The BaseCameraLifecycleObserver class is mainly used for inheritance by othersIt contains some basic camera initialization content
It also handles some lifecycle-related content
(e.g., handling the camera according to the lifecycle)
It also provides external methods to manually turn the camera on or off
cameraProviderDeferred
Worth mentioning is the use of cameraProviderDeferred hereIt is used to obtain ProcessCameraProvider
Since this operation is time-consuming, asynchronous operation is used for more flexibility
(However, I have also tried directly instantiating ProcessCameraProvider
In most cases, it is not easy to encounter ANR or stuck situations
Only occasionally 1 or 2 times on older models, such as Android 5.0)
The concept here is
CompletableDeferred uses .apply
Within the apply scope, it creates ProcessCameraProvider
Use `await()` to wait where needed
Achieving asynchronous operations while waiting for the actual creation before proceeding
The difference between completableDeferred and regular Deferred is
It can be manually controlled to complete using complete()
Which is suitable for this example
Need to wait for the ProcessCameraProvider listener to return
To know that initialization is complete
Code Explanation
ScannerLifecycleObserver is relatively simpleInherits from BaseCameraLifecycleObserver
Mainly writes features that might be needed based on project requirements
Such as some extended content
Like getCameraDisplayOrientation
Can be used to adjust the supported resolution of the camera
Or getImageAnalysis to get ImageAnalysis
ImageAnalysis is mainly used in MLKit to set which barcode types can be parsed
Code Explanation
ScannerAnalyzer is used to implement barcode parsingInherits from BaseCameraLifecycleObserver
Since we are parsing QR codes, we use FORMAT_QR_CODE